Mon - Fri 9.00 am - to 06.00 pm.
STYRAX CONSULTANTS PRIVATE LIMITED
Mon - Fri 9.00 am - to 06.00 pm.
STYRAX CONSULTANTS PRIVATE LIMITED
Competency Mapping is a process to develop competency framework for superior performance in context of the job being referred to predict performance. We develop both
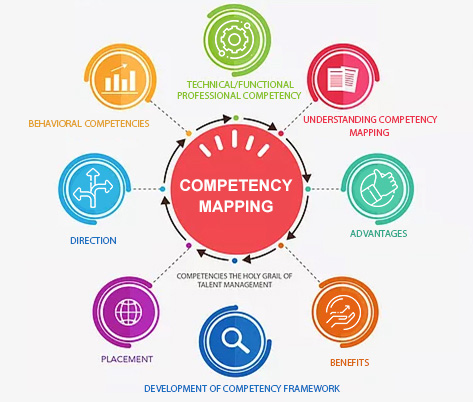
Behavioral competencies define how an individual performs in their role. These are sum of traits, abilities and motivations needed to deliver effective performance, regardless of your job in an organization. Behavioral competencies provide a substantial set of behaviors which aligns an organization’s vision or objectives with measurable behaviors which can aid in achieving organizational success
Technically competencies are what a person can do. They define hard skills, and specific knowledge. These types of competencies are closely aligned with the knowledge and skills or “know-how” needed for successful performance.
These technical/functional/professional competencies tend to be specific to roles or jobs within a Job Family, and include the specific knowledge and skills needed for optimal employee performance (e.g. specialized skills or career relevant knowledge).
These competencies can be specific to roles, levels or jobs within a Job Family or generic to a Job Family.
The Competency framework defines the competency and indicators( Behavioural& Technical) that are needed to produce results. Competencies are components of a job which are reflected in behaviour that are observable in a workplace. The common elements are knowledge, skills, abilities, aptitudes, personal attributes that impact performance at work. The criteria of competency are superior performance in context of the job being referred to predict performance.
Threshold competencies: These are the essential characteristics that everyone in the job needs to be minimally effective, but this does not distinguish superior from average performers.
Differentiating competencies: These factors distinguish superior from average performers.
When identifying the competencies, best practices are to limit the number to six to ten most important competencies. These numbers allow the insertion of the most significant behaviours on one hand while making use of competency models and their application manageable on the other hand. Competencies generated can be divided in one of three classifications:
Core (Organizational): Core competencies are defined as behaviours essential or “core” to the organizations
Universal/ Generic/ Common: Universal/ Generic/ Common competencies are those behaviors “common” to a job family. For the HR job family
Critical: Critical competencies are those behaviors specific to a job within a job family. For example, critical competency for HR manager – influencing skills.